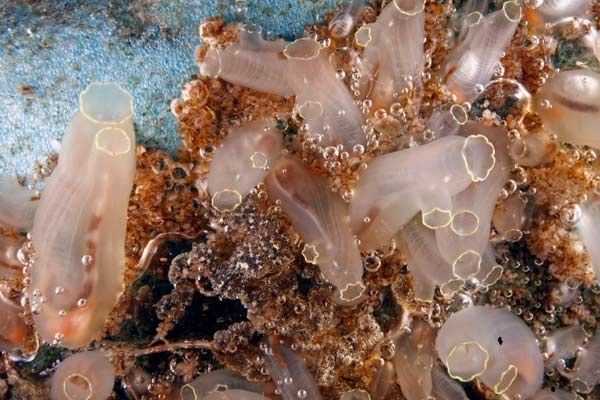

CHORDATA
Tunicata
[© Arjan Gittenberger]
Chapter Outline
Links to external sites will appear in pop-up windows.
"The strictly marine Urochordata or Tunicata are commonly known as tunicates, sea squirts, and salps. There are roughly 1,600 species of urochordates; most are small solitary animals but some are colonial, organisms. Nearly all are sessile as adults but they have free-swimming, active larval forms. Urochordates are unknown as fossils.
Evidence that tunicates are chordates comes clearly from the larval "tadpole" stage which shows pharyngeal slits and arches, dorsal hollow nerve cord, notochord and post-anal muscular (unsegmented) tail. Adults of most members are sessile filter feeders with an expanded pharynx and, like cephalochordates and larval lampreys, with an endostyle, a mucous food trap in the pharyngeal floor that is homologous with the thyroid gland of vertebrates."
[Chordata. John G. Lundberg. The Tree of Life Web Project. http://tolweb.org/tree?group=Chordata&contgroup=Deuterostomia. 1995.]
As of 2024, 111 species of Tunicata have been observed in iNaturalist in the US and 496 throughout the world.
Organisms:
- CLASS APPENDICULARIA
- CLASS ASCIDIACEA
- ORDER APLOUSOBRANCHIA
- Atlantic Sea Pork (Aplidium stellatum)
- ORDER PHLEBOBRANCHIA
- Yellow Sea Squirt (Ciona intestinalis)
- ORDER STOLIDOBRANCHIA
- Star Tunicate (Botryllus schlosseri)
- ORDER APLOUSOBRANCHIA
- CLASS THALIACEA
- ORDER DOLIOLIDA
- ORDER PYROSOMATA
- Pyrosome (Pyrosoma atlanticum) - most iNat observations in the US for Tunicata
- ORDER SALPIDA
- Twin-Sailed Salp (Thetys vagina)
- ORDER DOLIOLIDA
| Resources: |
| [ Previous Page ] | [ Next Page ] |